3.20 Consensus Algorithm
As the founding chain in Armonia's multichain network, AMC serves as the trust anchor and value engine to all the other spawned child chains. For those who adopt $AMAX as the native token of their own chains for basic functions like paying transaction fees, it is critical to ensure the security and reliability of the Armonia meta chain. This means sufficient decentralization and anti-censorship capability is required, as follows:
There should be enough copies of blockchain data maintained by mining nodes so that even if the mining nodes are under direct attack, the network can survive, operate and eventually return to a stable working state;
When there are vicious nodes trying to sabotage the network, the activities can be discovered and even corrected - as long as the total number of bad actors is below 1/3 of the total set of validators; and
Those mining nodes can be replaced by standby nodes when they are off-duty.
Armonia has developed a new consensus algorithm, known as Armonia DPOS (or, shortened to APOS), for the AMC chain, the mother chain and the other child chains can adopt their own consensus algorithm to protect their network.
The core framework of APOS is as follows:
All network nodes that run
AMCnode software can participate in block production for both main and blocks that formAMCmain and backup chain(s);The nodes elected through a non-stop voting process and rank top
21in the list become the main nodes and the remaining10,000nodes are the backup nodes;The voting process requires the candidate nodes to stake a certain amount of
$AMAXtokens in order to receive votes from the Armonia community;The other nodes either in the main or backup node list are called observer nodes;
The main nodes take turns according to VRF algorithm to produce main blocks and receive newly inflated
$AMAXtokens;The backup nodes also take turns according to VRF algorithm but are applied in a much larger quorum (10,000 nodes for one backup chain) and each backup block mined will reward the miner with a certain amount of
$AMAXtokens. The backup block must refer to the latest main block being produced by the main node;The main nodes shall include backup blocks when generating a main block and will be rewarded for correctly including a good backup block;
When a bad backup block is included in the main block, it will not be accepted by the whole network and thus discarded by other nodes;
When a main block is missing or faulty, the backup block will replace the main block to become the actual main block and the producer node thus receives the main block reward;
The finality of main blocks is determined through implementation of an
aBFTalgorithm. However, the finality of backup blocks is determined by the main blocks;Transactions with main blocks must be not only verified but also executed to update the corresponding global state of the network, while the backup blocks are only required to be verified in order to be accepted by the whole network. In this way, it avoids the double-spending problem and allows for the nodes to conduct parallel processing for both main and backup blocks; and
To prevent greedy or lazy nodes from cheating the network by producing empty or useless blocks that include useless fabricated transactions, reward to the backup nodes for producing backup blocks will correspond with the similarity of block transactions compared to those in the main blocks at the same height. Therefore, the reward will only be calculated and settled in the next block height.
The interwoven main and backup AMC chains may have the following block generation scenarios:
In general the main and backup blocks are interwoven as follows:
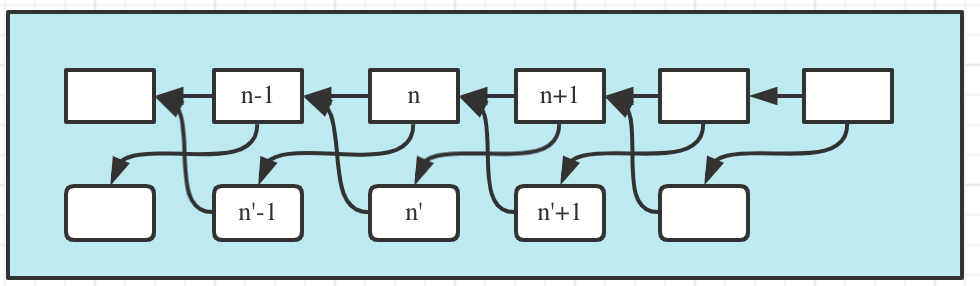
One Armonia main node produces 6 blocks in a row before shifting to other main nodes. But backup nodes shift each time after producing only one backup block:
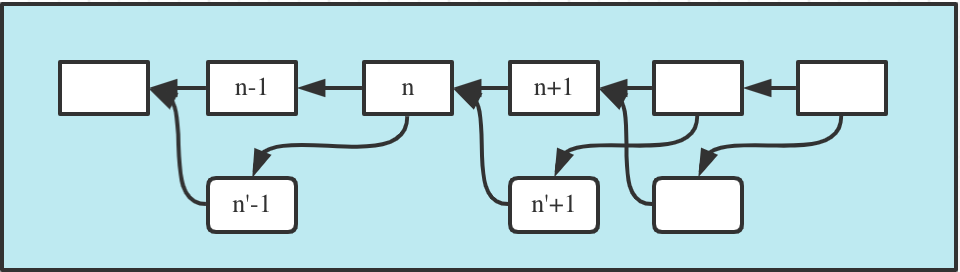
If the on-duty backup node is unable to produce the block of a timeslot, the next main block won't include the backup block:
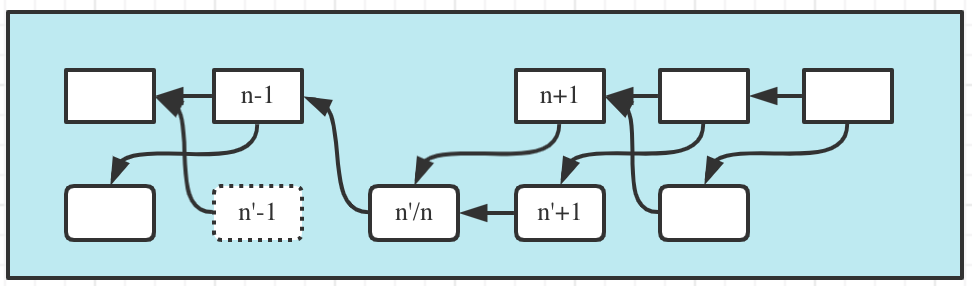
If the on-duty main node is unable to produce the block of a timeslot, the next (
n+1) main block will take the current backup block as the main block and its producing node will be rewarded with the amount of the main block reward. However, the prior (n'-1) backup block won't be rewarded as no main block is included:
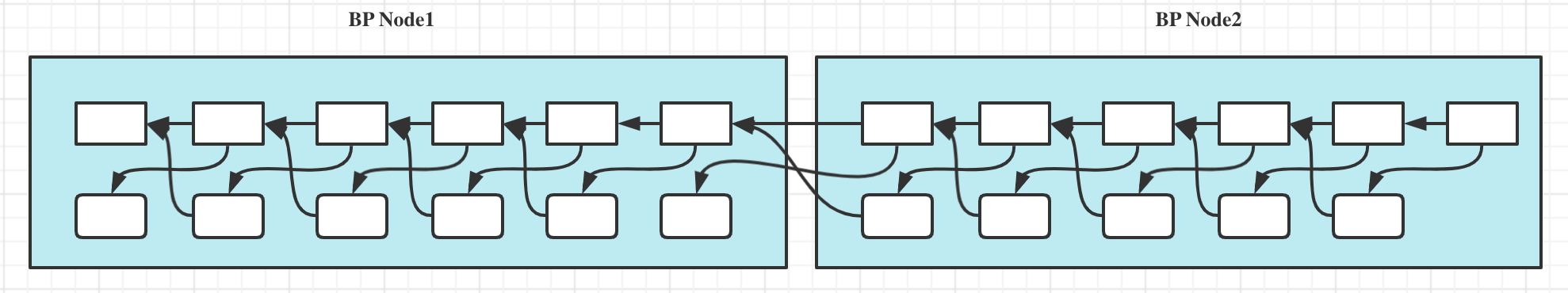
To summarize, the AMC chain can be composed of one main chain and zero to several backup chains that includes in total 21 + 10,000 * n number of mining nodes. Unlike a pure DPOS consensus algorithm that rewards candidate nodes that don't run the node software, APOS only rewards those that run the node software, synchronize with the network and actually produce main or backup blocks. This way, it greatly improves the overall security of the AMC chain.
With more backup nodes to participate, even though each backup node might get a reduced chances to mine blocks and thus mine fewer $AMAX, the overall network security and community consensus is enhanced and will eventually enchance the $AMAX token value. This will encourage more users to participate and further increase the awareness of the project. As for the number of backup chains, it can be decided by DAO governance mechanism.
Voting for mining node election will not start during the first year of its inception as the AMC chain will be undergoing a fast-pace development and will likely upgrade its mode. Therefore, the original 21 main nodes will not yield any new $AMAX token upon each block production. Voting is expected to be open to the public after passing v1.0 milestone and new tokens will be minted/inflated after all staked and voted $AMAX tokens reach more than 5% of the total supply.
Last updated